Synapse Group
|
|
|
|
Synapse groups represent a unified construct allowing users to interact with the aggregated whole of all the synapses connecting two Neuron Groups. In very large networks, operating on synapses on an individual basis would be impractical; Synapse Groups offer a means by which users can manipulate all synapses with common source and target destinations. This includes things like mass manipulation of synapse properties, learning rules, and the display of synaptic strength data. Synapse groups automatically organize and separate synapses by their polarity (i.e. whether or not they are excitatory or inhibitory, as determined by the sign of their weight value). Therefore the excitatory synapses in a synapse group may be manipulated independently of the group's inhibitory synapses.
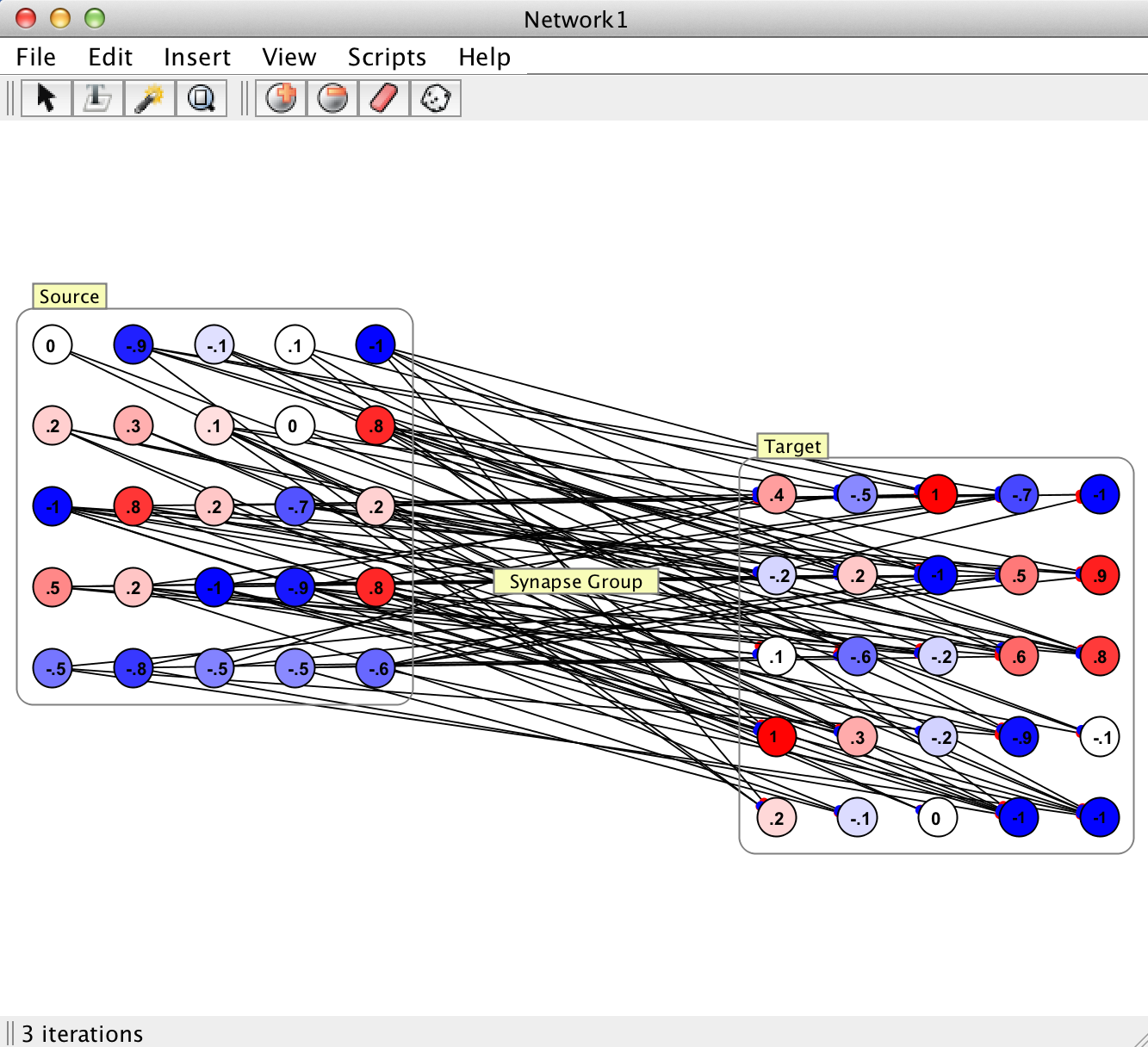
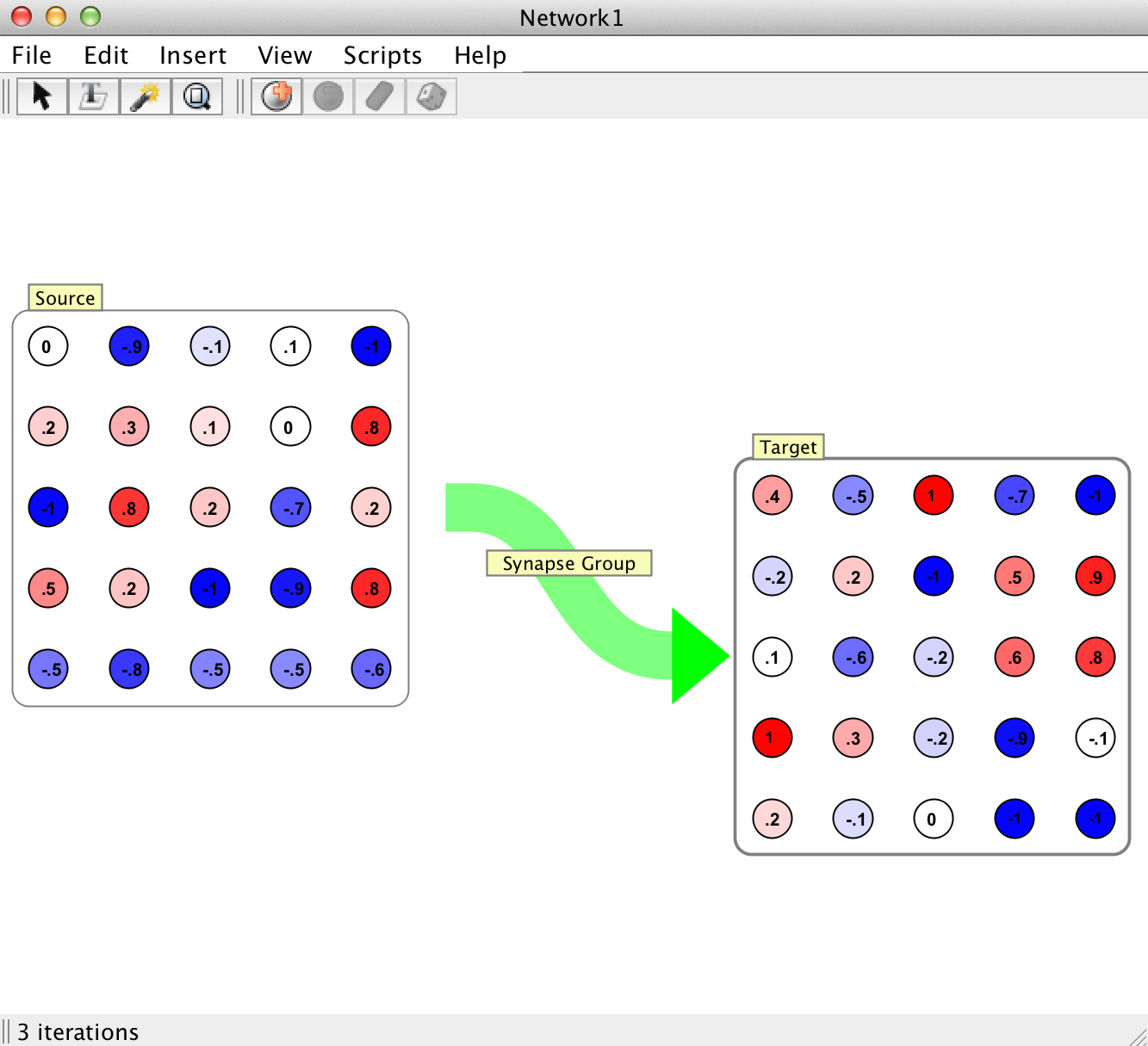
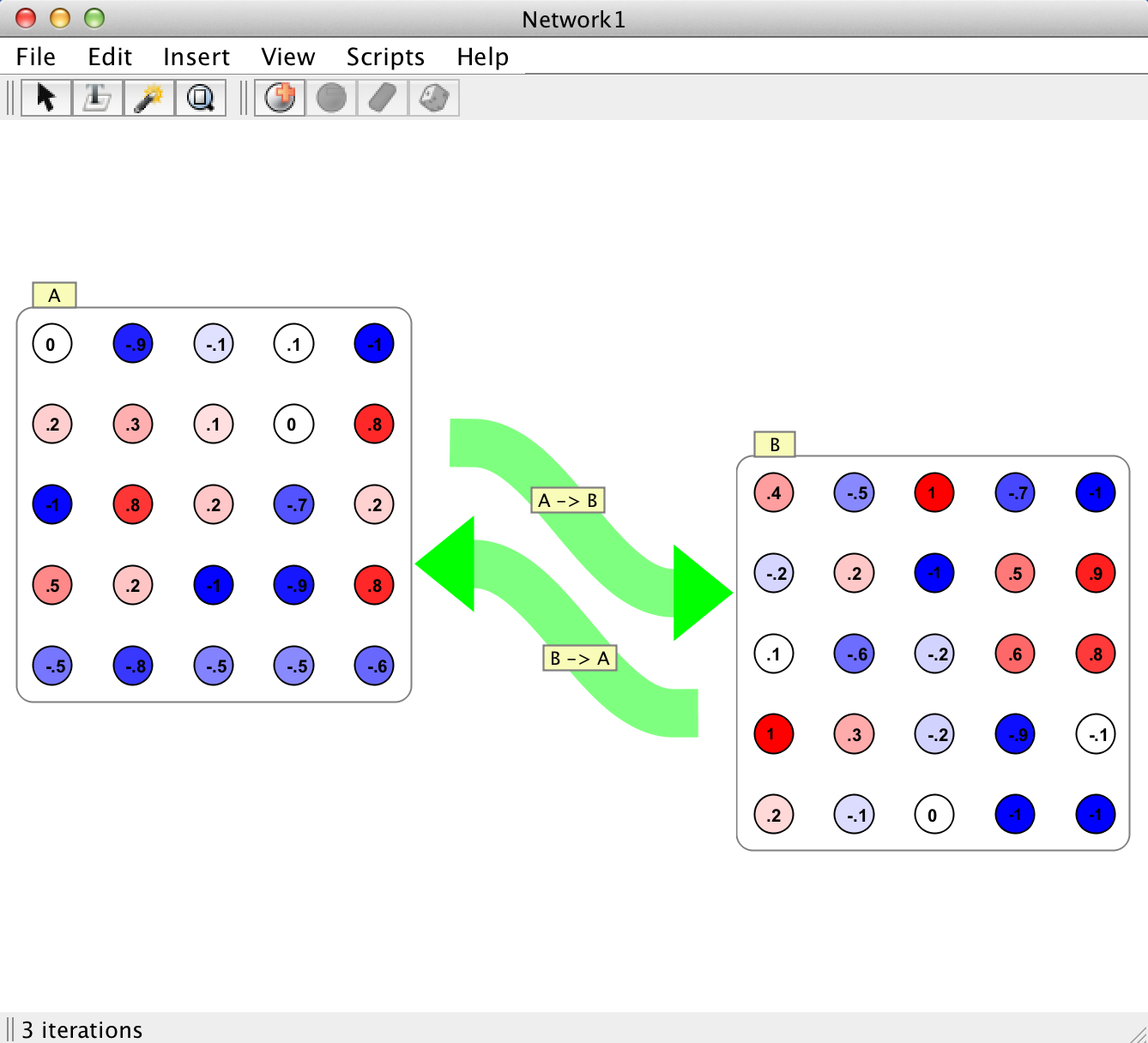
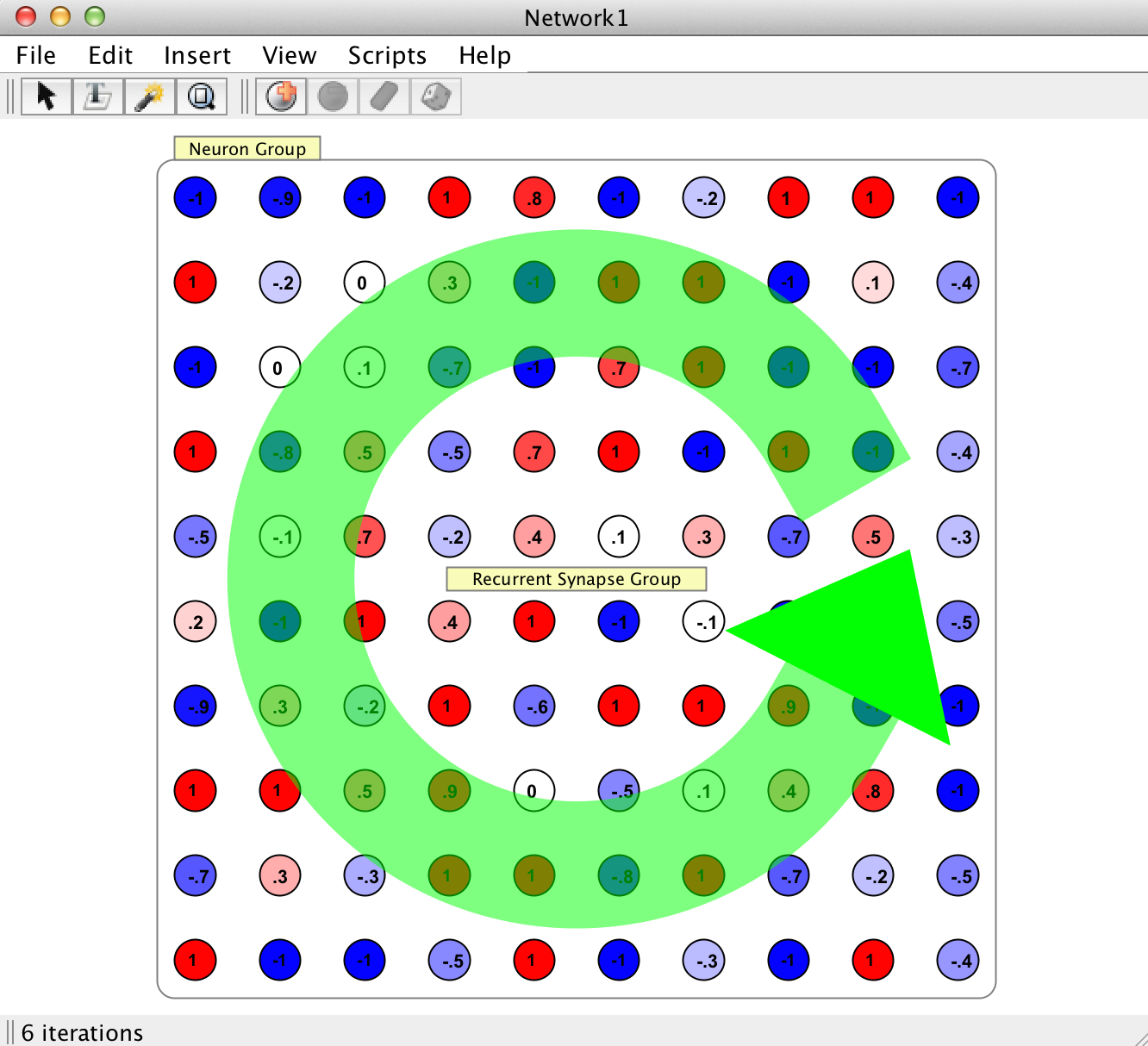
Pictured here is an example of all the different visualizations of synapse groups a user may encounter in Simbrain. Although there are different visualizations for unidirectional, bidirectional, and recurrent synapse groups, it is important to note that fundamentally they all represent the same underlying construct.
Synapse Visibility
By right clicking any synapse group interaction box, the user has the ability to "toggle synapse visiblity". Toggling synapse visibility either reveals each of the individual synapses constituting the group.
Visible synapses: In this mode (first of the four images here) all synapses can be seen, and can be directly edited like synapses generally are. However, these are not loose synapses. They are still members of a group and so it is suggested that they be interacted with primarily at the group level, via the interaction box.
Momentum: Here the group of synapses is replaced by a green arrow with an interaction box inthe center. This is the preferred mode of dealing with large groups of synapses.
Note: For very large synapse groups (> ~10,000) it is not advisable to make each indvidiual synapse visible. In such cases the connectivity structure is obscured by the sheer number of synapses, and worse, the GUI may become slow or unresponsive (depending on the machine and how many synapses are being made visible at once).
Synapse Group Creation
To manually create a synapse group, select the source neuron group by its interaction box, designate it as a source neuron group (either by pressing "1" or invoking the set as source menu command), and then select a target neuron group by selecting it, and invoke the synapse creation dialog (either by pressing "2" or invoking the Connect Neuron Group with Synapse Group command). Cf the quick 1 2 method for neurons. The same thing works when manually connecting neuron groups with synapse groups.
Before the actual synapse group is created a synapse group creation dialog will appear.
Synapse groups are also parts of subnetworks and are automatically created when most subnetworks are created.
Synapse Group Creation and Edit Dialogs
When creating a synapse group or editing one, a dialog shows up that allows many features to be viewed and edited. The tabs of this dialog are described on this page and on the weight visualization page.
Synapse Group Properties
The basic information that synapse groups store and maintain on the group level and about their constituent synapses includes the following:
Group ID: Unique labelling that identifies the group.
Label: Name of group, which is editable by the user.
Population: Number of synapses in the group.
Optimize As Group: An advanced option for speeding up the data representation and update speed of synapse groups. When a synapse group has this option selected, it maintains prototype excitatory and inhibitory synapses, which it pulls data from in order to display information about the group. This is as opposed to iterating over every synapse in the group and checking a particular value to ensure all synapses have the same value. Similarly, when updating the synapse group, iteration over synapses of a given polarity will be skipped entirely if the prototype of that polarity indicates that the synapses of that type are frozen or static. This feature assumes that if the user is working whe synapse groups, then their interaction with individual synapses will be minimal. If a single synapse were to be changed independently of the synapse group tools for doing so, those changes would not be reflected in the synapse group dialog.
Excitatory Type: The type or update rule governing the excitatory synapses in the group. See the page on synapses for a complete listing.
Inhibitory Type: The type or update rule governing the excitatory synapses in the group. See the page on synapses for a complete listing.
Parent: Denotes the parent group, if any.
Source/Target Group: The neuron group which acts as a source(target) to this synapse group. Specifically the whole of the synapses comprising this group represent the efferent(afferent) synapses of the source(target) neuron group, which connects the source group to the target group. In other words a given synapse group mediates the flow of activation between its source and target group. It should be noted that there can be no more than 1 synapse group connecting two neuron groups in a particular direction. That is, there cannot be more than one synapse group with the same source and target neuron group.
Synapse Group Types
Synapse groups allow users to edit en masse the properties of the synapses that comprise the group. This includes the basic properties like delay, or bounds, but also the synapse update rule(s) and spike responder(s) and its(their) own independent properties. Since synapse groups segregate synapses by polarity, these changes can be applied to excitatory or inhibitory synapses independently. For a full listing of the properties of synapses which can be changed see the page on synapses. Synapse groups allow you to manipulate all the synapses in the group as you would an individual synapse.
Connection Types
During creation, the user must choose which type of connection type should be used to determine how (and what) synaptic connections are made. For a full listing as well as links to the details of how each connection manager functions, see the page on connections.
Synapse groups allow users to edit some properties of the overall connectivity structure of the synapses in the group. In some cases like sparse, users can manipulate the connection density of the synapse group after creation. Otherwise, it is not an option to edit the connection manager post-creation.
This tab is covered in the weight visualization documentation.
Edit: Edit group properties. This opens the group properties panel which includes the above sections. The is the same as double-clicking on the interaction box.
Remove Group: Delete the group.
Select Synapses: Select all neurons in the group. Suggest using this primarily when synapses are visible
Select Incoming Neurons: Selects all pre-synaptic neurons for synapses in this group.
Select Outgoing Synapses: Selects all post-synaptic neurons for synapses in this group.
Adjust synapses: Opens the synapse adjustment panel for this group of synapses. But note that it is suggested that the synapse group dialog be preferred for this kind of manipulation and visualization..
Show Weight Matrix: shows the weight matrix viewer for this grouof synapses.
Freeze / Unfreeze synapses: Freezes or unfreezes all synapses in this group. Learning will cease.
Enable / Disable synapses: Enables or disables all synapses in this group. They will stop passing information along; functionally equivalent to (temporarily) removing the group.
Toggle synapse visibility: Toggles synapse visibility.
Connect Neuron Group with Synapse Group: Connect source and target neuron groups with a synapse group.
Send Vector Coupling To: Copies all strengths in the group and represents them as a flat vector (matrix couplings are not currently supported). This creates a coupling such that this vector is forwarded to some other component in Simbrain. See the couplings page.
Recieve Vector Coupling from: Takes some vector forwarded from some other component and sets the weight strengths of the synapses in this group based on the incoming vector.