Hopfield Network
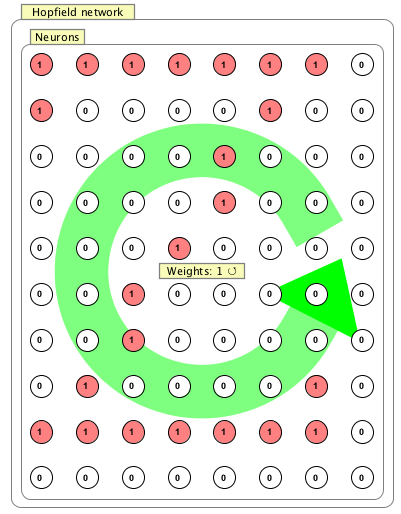
A discrete hopfield network is a collection of binary neurons that are recurrently connected to each other. They are useful in pattern completion tasks: a Hopfield network stores a number of "memories" (e.g. the network shown stores the letter "Z") and can retrieve these memories from partial patterns. Hopfield networks have certainly analytical properties that make them ideal for mathematical analysis.
To get a feel for how Hopfield network works open the Hopfield simulation and follow the included directions.
Creation / Editing
Hopfield networks are initialized with some number of units, and are by default laid out as a grid. They are fully interconnected with no self connections.
Number of Neurons: Set desired number of neurons in this field.
Update Order: This can be set to random or sequential. If set to random, the neurons are updated in random order. This is the standard assumption of Hopfield networks. if sequential is used, neurons are updated in the same sequence each time, making it possible to reproduce chains of behavior.
By Priority: (Only for sequential).Use neuron priority fields when updating sequentially.
Shuffle Order: (Only for sequential) Shuffle the order of the sequential update.
Training
To train a Hopfield network double click on the interaction box, load training data using the input data tab of the training dialog, and then press the play button.
Right Click Menu
Update Order:This can be set to random or sequential. If set to random, the neurons are updated in random order. This is the standard assumption of Hopfield networks. if sequential is used, neurons are updated in the same sequence each time, making it possible to reproduce chains of behavior. Three cases:
- Synchronous does not depend on the order in which nodes are updated but sometimes produces oscillations
- Sequential is more stable. Nodes are updated one at a time and order matters. More stable than synchronous. Can either use the priority [link] of the nodes for update order, or a random order (randomize once at initialization and use this order every time).
- Random: nodes are updated in random order. This was important in the history of Hopfield networks and is related to Boltzmann machnes.
Add Current Pattern To Input Data: Add the current pattern in the network to the training set. Useful for creating training data directly in the GUI.
Randomize Synapses Symmetrically: Randomize the synaptic weights symmetrically.
Set Weights To Zero: Set all synaptic strengths to zero.
Edit/Train Hopfield: Open the edit / train dialog.
Set Weights To Zero: Set all synaptic strengths to zero.
Train on current pattern: Trains the Hopfield network using the Hebb rule to learn the current pattern of activity across its nodes.
Continuous Hopfield Networks
To create a continuous Hopfield network use a set of Additive neurons in a standard network. These can be connected appropriately and trained by using Hebbian synapses. The user then clamps all neurons, iterates to train the synapses, then clamps all weights. On clamping, see toolbar.
References
See the Scholarpedia article on Hopfield Networks.